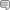 0
comments
Friday 28 September 2012
0
comments
Friday 28 September 2012
This photograph appears in 'Dr John Clifford, C.H. Life, Letters and Reminiscences' by Sir James Marchant, LL.D., first published in 1924, opposite page 218. Dr John Clifford was born at Sawley on 16 October 1836. John Clifford rose from a twelve hour per day child apprenticeship in a large factory through university exams in arts, science, and law to outstanding leadership in the Baptist Christian community. Among his fellow Baptists he was considered a progressive influence theologically. Socially, he frequently sided with radical movements, as evidenced by his membership in the Fabian Society. Politically, he exercised great influence on several pieces of legislation relating to education; he was a known supporter of David Lloyd George. In many ways, Clifford was the father of social Christianity among Free Churchmen in Great Britain. He used his Baptist conviction of religious liberty to advance his feeling that the message of Christ should be interpreted in light of growing knowledge and experience. He opposed, for instance the 'living-in' system of apprentices and later the atrocities perpetuated by the Belgians upon the Congo peoples. In 1885 his church established a home for unemployed women, and for more than thirty years he led in the temperance crusade to close public houses where neighborhood sentiment was in strong opposition. Clifford's attitude about the new interpretations of the Bible soon put him into conflict with Charles H. Spurgeon. The pastor at Praed Street had long urged attention to Darwin's work and German higher criticism, two issues Spurgeon saw as symptomatic of the 'down-grade' of Baptist life and thought. Eventually, Spurgeon withdrew from the Baptist Union in 1887, and Clifford was subsequently elected its president. In his inaugural address in 1891 he addressed the topic 'The Coming Theology'; he argued for the increase in the unity of humanity and a greater appreciation for Christianity. To Clifford's credit, he became the symbol of global Baptist leadership moving into the twentieth century. His openness led to significant positions in both the Baptist World Alliance and the Evangelical Free Churches in Great Britain. It was the issue of church-related primary and secondary education which made Clifford a powerful influence in the making of public policy. In the 1870s he welcomed legislation that created religious education in private schools. Clifford reasoned that the 'conscience clause' deprived schools where such instruction was offered of the right to public revenues. For this reason, in 1902 when a second Education Bill provided increased support for religious education in public schools, Clifford protested loudly and led a large-scale 'passive resistance' to the legislation. The preacher, who was largely credited with overturning the bill, had planned to protest with all his might against teaching a set of dogmatic theological opinions. He wished theological dogma to be taught, but by the churches, and at the expense of the churches. Clifford's literary output was remarkable. He penned ninety-nine books or pamphlets, edited denominational newspapers, and carried on a voluminous correspondence. His contributions were honored by heads of government and institutions; in 1883 Freewill Baptist Bates College in Lewiston, Maine, conferred on him in absentia an honorary doctorate. Sensitive to British opposition to 'bogus American degrees,' Clifford gracefully declined, preferring to be known as 'the pastor of Praed Street, Paddington'. (information from the 'generalbaptist' website)







